Reconstitution of human T regulatory and NK cells in a Novel IL2-humanized NCG mouse model
June 15, 2024
Reconstitution of human T regulatory and NK cells in a Novel IL2-humanized NCG mouse model
T regulatory cells (Tregs) are a specialized subpopulation of T cells that suppress the immune response by inhibiting T cell proliferation and cytokine production. Natural killer (NK) cells are the predominant innate immune subset that mediates anti-tumor and anti-viral responses. Both Tregs and NK cells are critical immune cells that play an important role in cancer immunotherapy. However, there is a lack of animal models that can be used to study the in vivo function of these two human immune subsets.
Interleukin-2 is a key molecule that promotes the expansion and activation of lymphocytes, including Tregs and NK cells. We knocked in the human IL-2 gene in the NCG mouse and developed an excellent severely immunodeficient mouse model, NOD/ShiLtJGpt-Prkdcem26Cd52Il2rgem26Cd22/Gpt (NCG-hIL2). The ability of this model to support Treg and NK cells was then compared to NCG using human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) and human hematopoietic stem cells (HSC) for reconstitution.
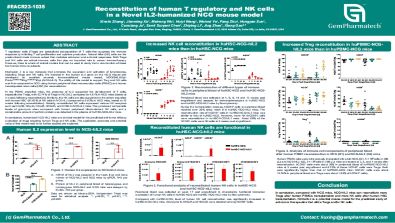
In the PBMC-engrafted mice, the presence of IL-2 supported the development of T cells, especially the Tregs, with 53.74% of Tregs in NCG-IL2 compared to 4.81% in NCG mice (tested at 2 weeks following reconstitution). Similarly, the NK cells are also supported in the cohort engrafted with human HSC (91.63% of NK cells in NCG-IL2 compared to 0.53% in NCG mice, tested at 10 weeks following reconstitution). Notably, reconstituted NK cells expressed various NK receptors such as NKp30, NKp44, NKp46, NKG2D, and CD94 in NCG-IL2 mice. They produced comparable levels of granzyme when compared with human peripheral blood-derived NK cells, and a considerable amount of perforin protein was detected in the plasma of huHSC-NCG-hIL2 mice.
In conclusion, humanized NCG-hIL2 mice are an ideal model for the preclinical anti-tumor efficacy evaluation of drugs targeting human Tregs and NK cells. The application scenarios and potential value of this model need to be further studied and explored.
Download
Interleukin-2 is a key molecule that promotes the expansion and activation of lymphocytes, including Tregs and NK cells. We knocked in the human IL-2 gene in the NCG mouse and developed an excellent severely immunodeficient mouse model, NOD/ShiLtJGpt-Prkdcem26Cd52Il2rgem26Cd22/Gpt (NCG-hIL2). The ability of this model to support Treg and NK cells was then compared to NCG using human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) and human hematopoietic stem cells (HSC) for reconstitution.
In the PBMC-engrafted mice, the presence of IL-2 supported the development of T cells, especially the Tregs, with 53.74% of Tregs in NCG-IL2 compared to 4.81% in NCG mice (tested at 2 weeks following reconstitution). Similarly, the NK cells are also supported in the cohort engrafted with human HSC (91.63% of NK cells in NCG-IL2 compared to 0.53% in NCG mice, tested at 10 weeks following reconstitution). Notably, reconstituted NK cells expressed various NK receptors such as NKp30, NKp44, NKp46, NKG2D, and CD94 in NCG-IL2 mice. They produced comparable levels of granzyme when compared with human peripheral blood-derived NK cells, and a considerable amount of perforin protein was detected in the plasma of huHSC-NCG-hIL2 mice.
In conclusion, humanized NCG-hIL2 mice are an ideal model for the preclinical anti-tumor efficacy evaluation of drugs targeting human Tregs and NK cells. The application scenarios and potential value of this model need to be further studied and explored.