The BDL-induced cholestasis model is a valuable platform for studying the pathophysiology of cholestatic liver disease and test potential therapeutic interventions. cholestatic liver disease. Bile duct ligation (BDL) blocks bile flow, leading to the accumulation of bile components in the liver and blood. This causes oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction in hepatocytes, activates Kupffer cells and neutrophils, and triggers the release of inflammatory factors (such as TNF-α and IL-6), resulting in an inflammatory response that further exacerbates liver injury. Additionally, chronic cholestasis activates hepatic stellate cells (HSCs), promotes the deposition of extracellular matrix (ECM), and ultimately leads to liver fibrosis and cirrhosis.
Experimental Design and Example Data
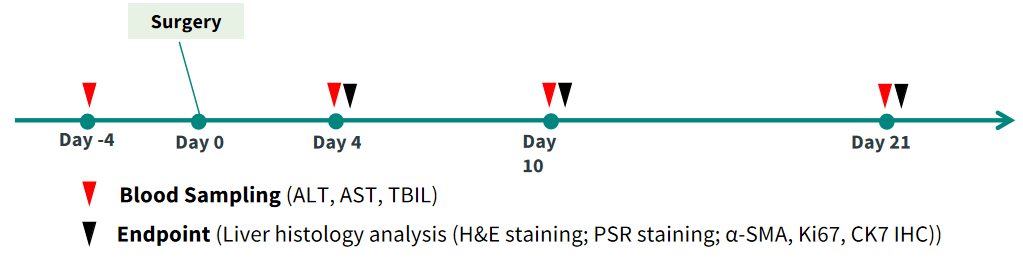
Study Design
Body Weight and Survival
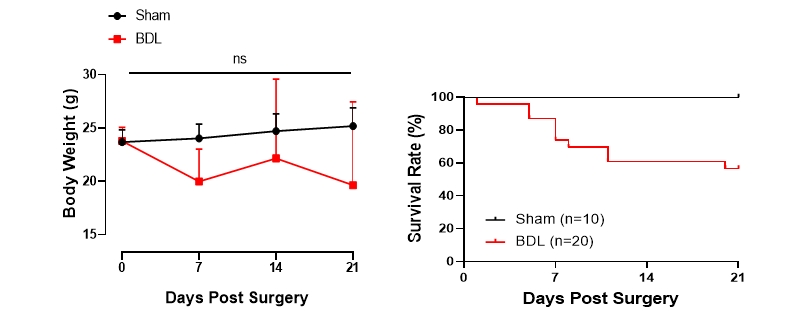
Figure 1. Following ligation, mice show significantly decreased body weight with approximately 60% survival rate at 21 days post-surgery.
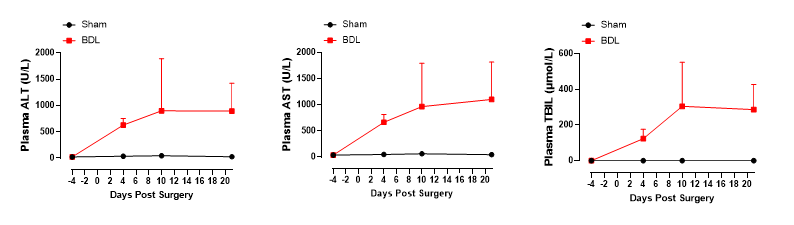
Figure 2. Mice show significantly increased indicators of liver damage (alanine transaminase, ALT; aspartate transaminase, AST) after BDL.
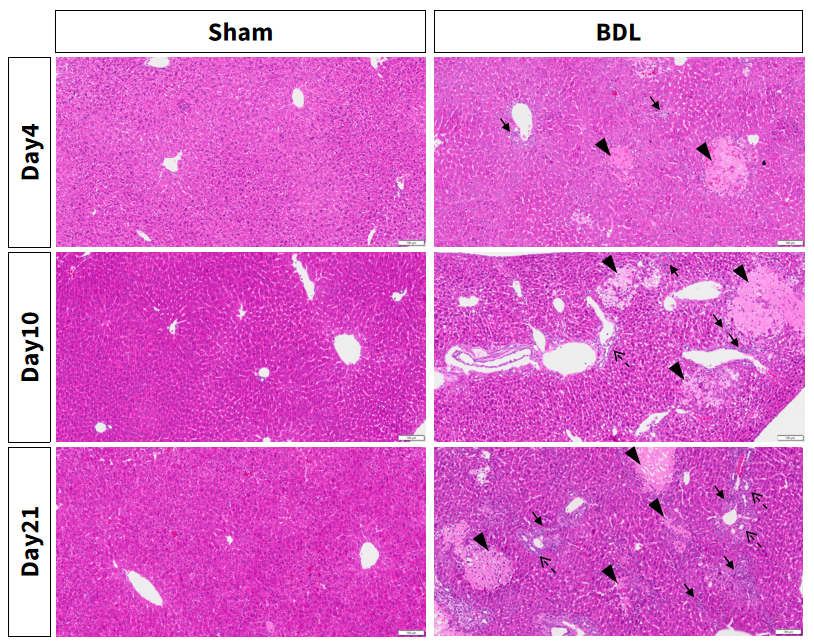
Figure 3. Bile duct ligation induces severe inflammation, necrosis and bile ducts proliferation.
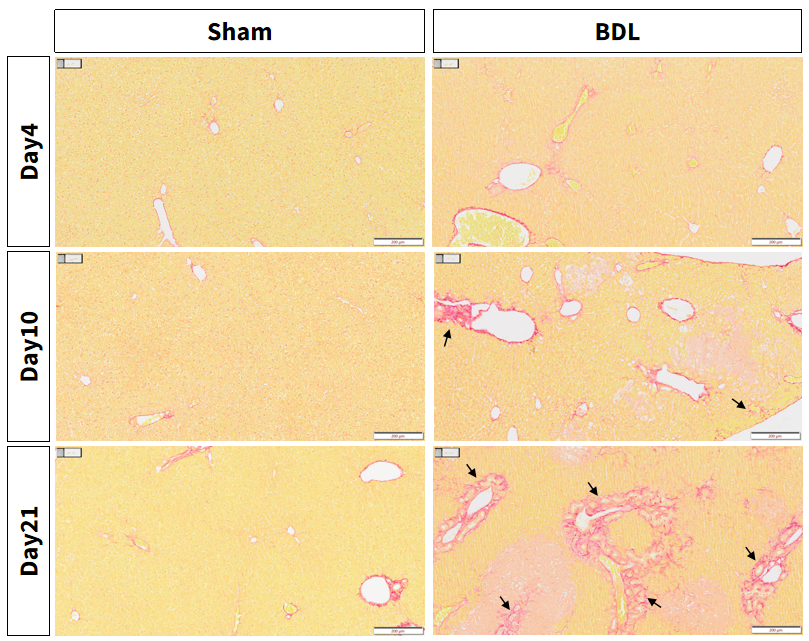
Figure 4. BDL-induced aggravation of liver damage: Bile duct ligation induces fibrosis around the portal vein.
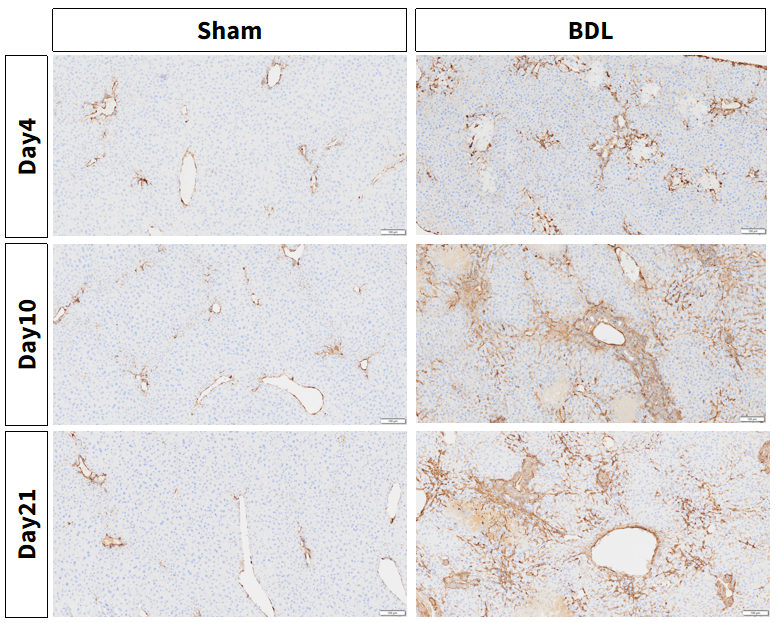
Figure 5. BDL induced aggravation of liver damage: α-SMA expression dramatically increased in the liver of BDL mice, indicating the activation of stellate cells.
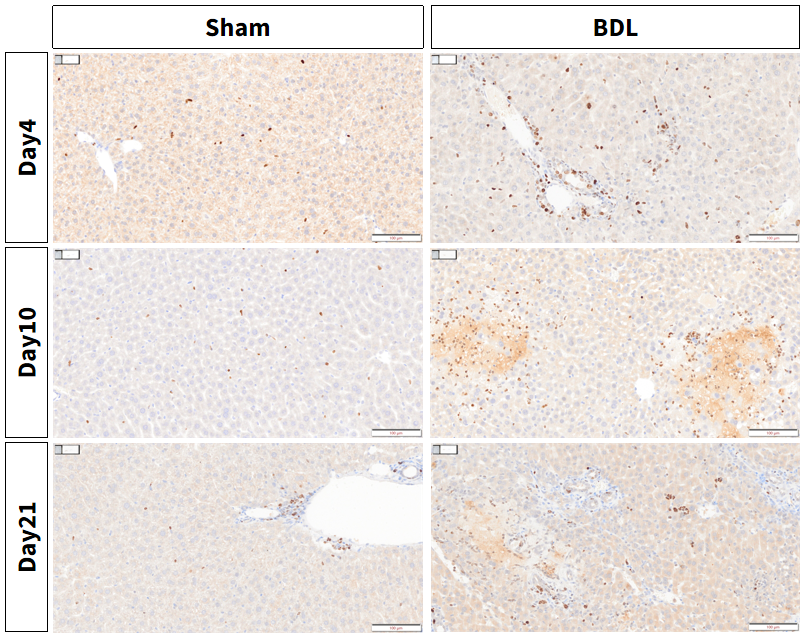
Figure 6. BDL-induced aggravation of liver damage: Increased intrahepatic expression of Ki67, a marker of proliferation, in the BDL model.
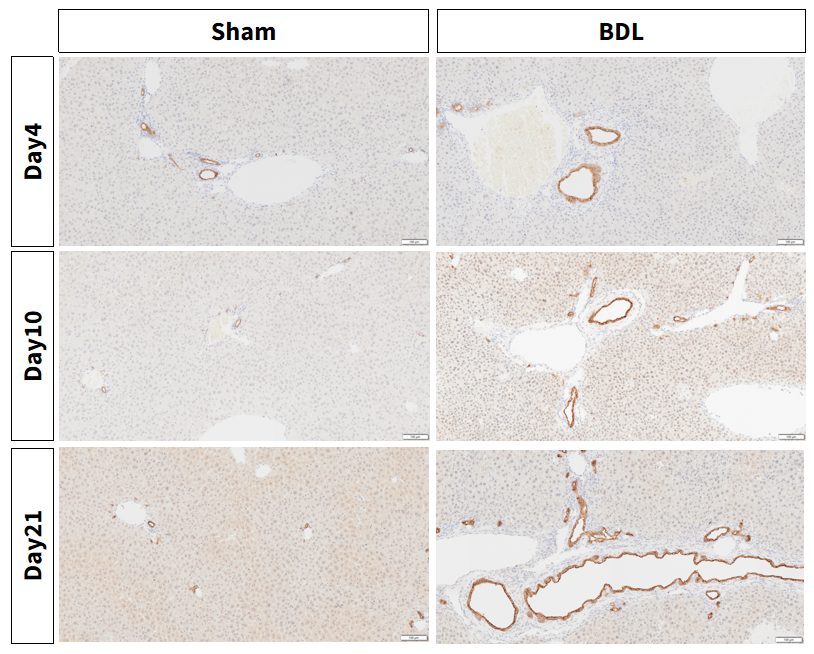
Figure 7. BDL induced aggravation of liver damage: Cholestasis and primary biliary cirrhosis marker CK7 are increased in the BDL model.