Lupus Nephritis is a serious kidney complication of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), an autoimmune disease. It occurs when autoantibodies form immune complexes that deposit in the kidneys, causing inflammation and damage to renal structures, particularly the glomeruli.
To aid with your preclinical studies, GemPharmatech has developed and validated a spontaneous model of lupus nephritis by overexpressing human B-cell activating factor (BAFF) in a C57BL/6J mouse.
C57BL6/J-hBAFF, a spontaneous lupus nephritis mouse model
The B cell activating factor (BAFF), or B lymphocyte stimulator (BLyS), is a B cell survival factor which supports autoreactive B cells and prevents their deletion. BAFF expression is closely linked with lupus nephritis and is enhanced by genetic alterations and viral infections. In C57BL6/J-hBAFF mouse, the human BAFF was sustained in high level and lupus nephritis is developed spontaneously.
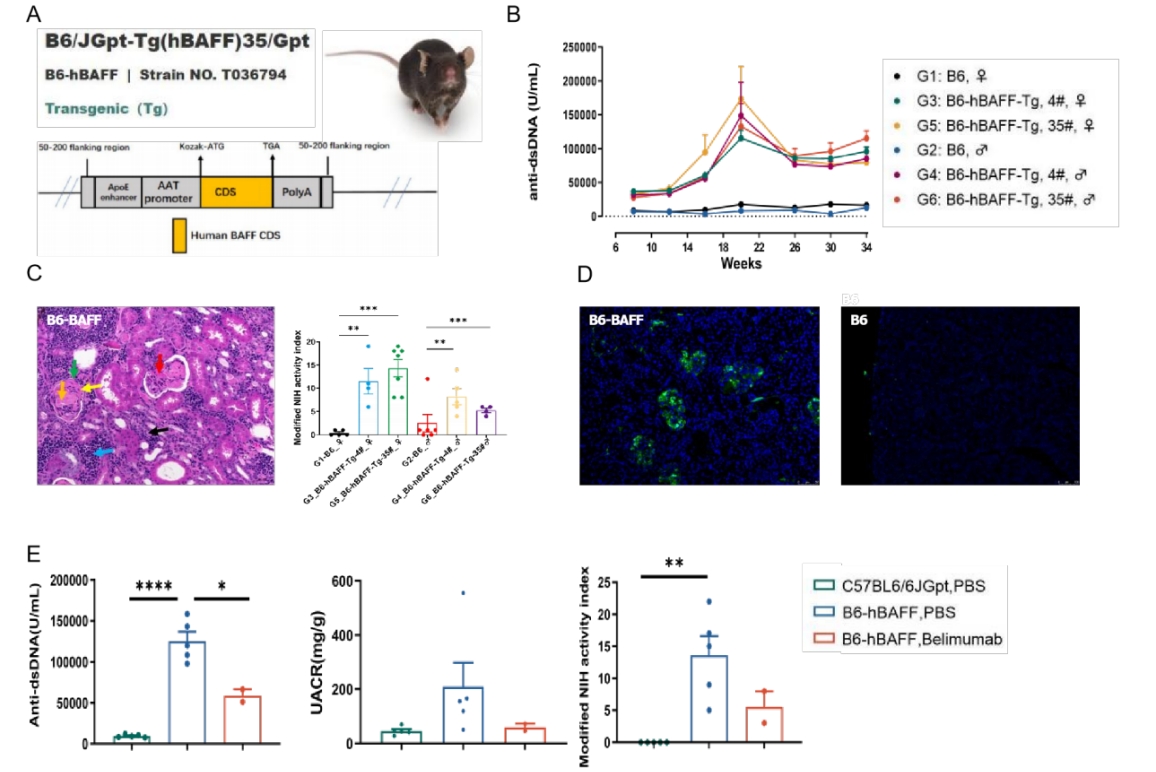
Fig 1. C57BL6/J-hBAFF mice present with a spontaneous lupus nephritis phenotype. A: the model strategy of C57BL6/J-hBAFF; B: high levels of serum anti-dsDNA in C57BL6/J-hBAFF mouse were observed from 6 week to 34 week; # refers to animal ID; C:, kidney biopsy (×200) shows glomerulus enlargement, immune complex deposition, segmental fibrinoid necrosis (↑), crescent formation (↑), peripheral renal tubular atrophy (↑), lymphocytes infiltration (↑), capsule adhesion (↑), and hyaline thrombus (↑); D: the deposition of immune complex in C57BL6/J-hBAFF kidney; E: The efficacy study of anti-hBAFF (Belimumab) on C57BL6/J-hBAFF lupus nephritis model. Significant remission was observed by the treatment of Belimumab accompanied with the decrease of UACR, serum anti-dsDNA and NIH scores. Data presented as mean ± SEM. *P<0.05,**P<0.01;***P<0.001.