Systemic sclerosis (SSc), also known as scleroderma, is a rare autoimmune connective tissue disorder associated with increased morbidity and mortality. It is characterized by inflammation and autoimmunity, vasculopathy, and fibrosis of the skin and internal organs. To aid with your preclinical studies, GemPharmatech offers several validated SSc mouse models.

Bleomycin-Induced Mouse Model
The SSc model induced by Bleomycin (BLM) is a classic animal model used to evaluate the preclinical efficacy of drugs for treating SSc. We utilized Bleomycin (BLM) to induce a scleroderma mouse model in C57BL/6J, BALB/c, and HSC-NCG-IL15 mice.
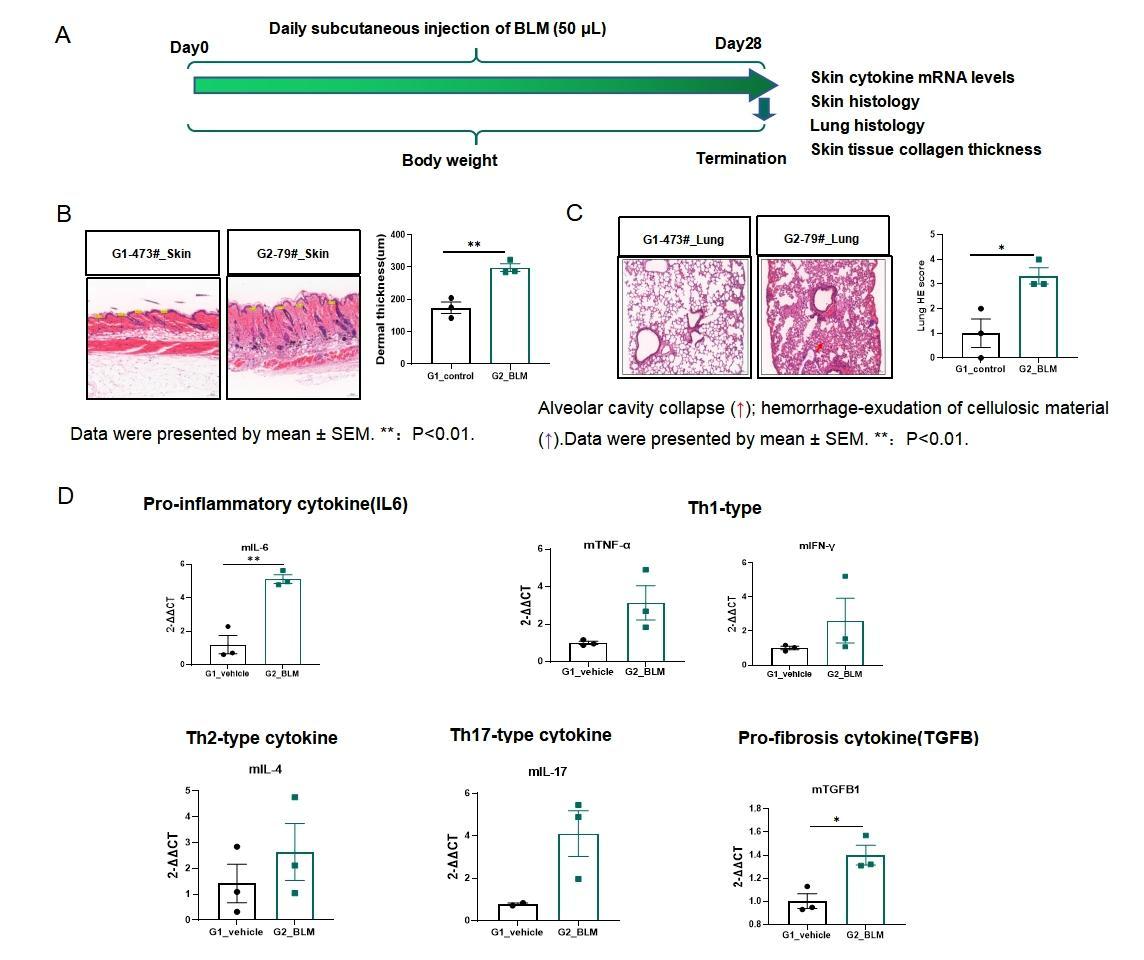
Fig.1 BLM-induced SSc C57BL/6J mouse model
The BLM-induced model strategy is shown in Fig.1A. After induction of B6 mice for 28 days, the dermal thickness of model group mice with BLM induction increased significantly (Fig.1B). Lung HE staining of the model group revealed inflammatory cells, alveolar cavity collapse, and hemorrhage - exudation of cellulosic material (Fig.1C). In the skin modeling area of the model group, the inflammatory cytokines increased significantly (Fig.1D).
Hypochlorous acid (HOCL) Induced Mouse Model
The pathogenesis in HOCl-induced mice is based on the oxidative stress theory, where injection of HOCl directly induced inflammation and fibrosis.
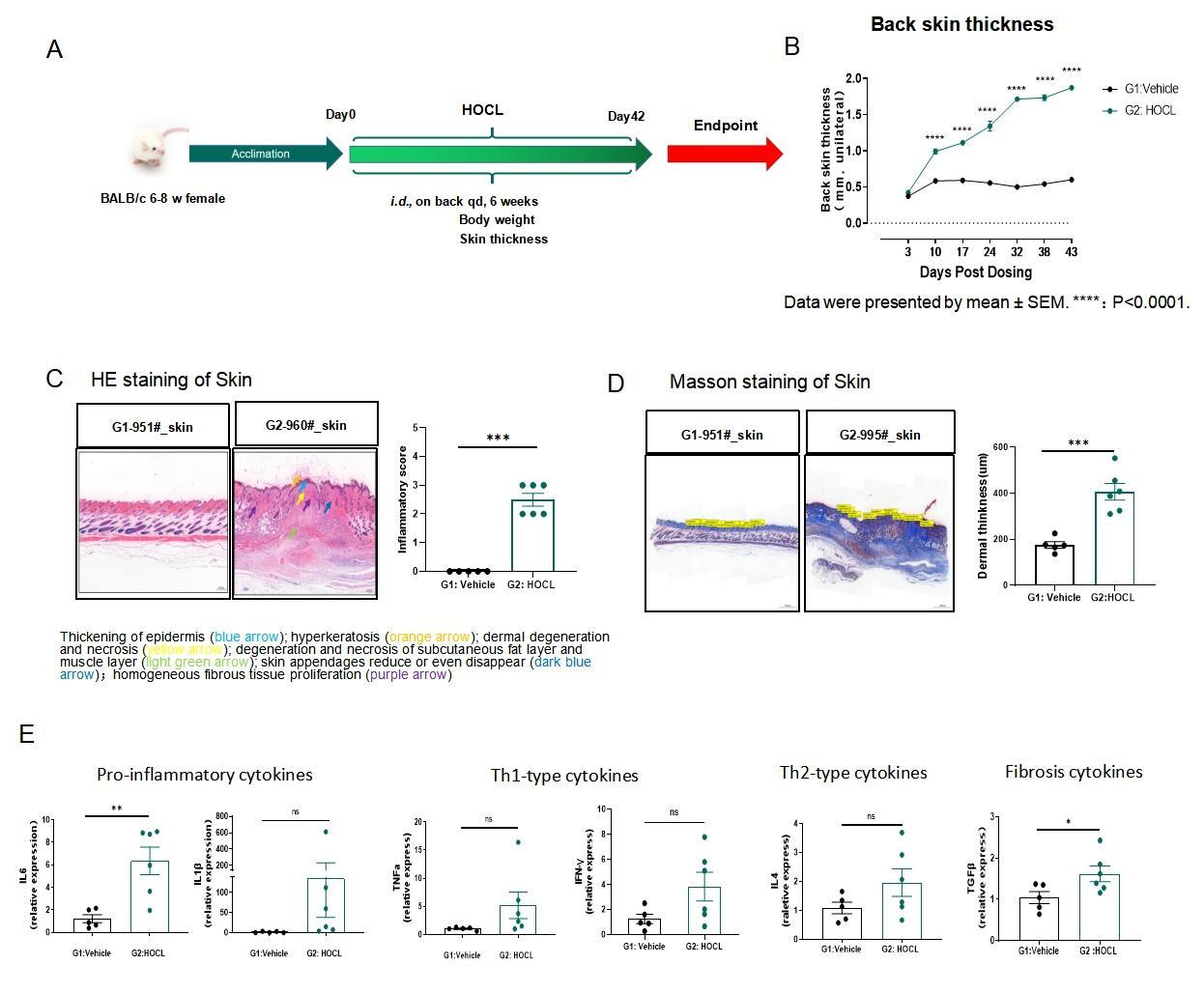
Fig.2 HOCL-induced SSc BALB/c mouse model
The HOCL-induced model strategy is shown in Fig.2A. After induction of BALB/c mice for 42 days, the back skin thickness and dermal thickness of model group mice with HOCL induction increased significantly (Fig.1B,D). Skin HE staining of the model group revealed inflammatory cells, hyperkeratosis, dermal degeneration and necrosis and other pathological changes. (Fig.2C). In the skin modeling area of the model group, the inflammatory cytokines increased significantly (Fig.2D).