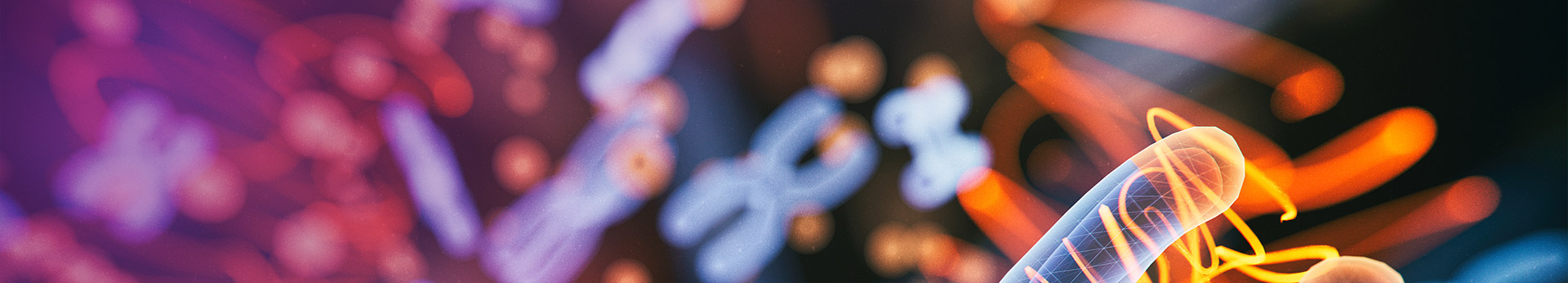Urticaria is an inflammatory skin disorder characterized by wheals, angioedema or both due to activation and degranulation of skin mast cells and the release of histamine and other mediators.
Passive Cutaneous Anaphylaxis (PCA) model induced in BALB/c mice
Mouse ears are injected with anti-dinitrophenol (DNP) IgE mAbs. These antibodies bind to FcεRI on mast cells, mimicking primary DNP antigen exposure and sensitizing mast cells and basophils.
Fig.1 Anti-DNP IgE-induced PCA BALB/c mouse model
PCA model strategy is shown in Fig. 1A. One hour post DNP-HSA administration, mice in the modeling group exhibited dye leakage in the ear (Fig.1B-C). HE staining revealed inflammatory cell infiltration, dermal edema, and epidermal thickening in the model group (Fig.1D). TB staining showed significantly increased degranulated mast cells in the model group (Fig.1E). Data presented as mean ± SEM. ***P<0.001.
Passive Cutaneous Anaphylaxis (PCA) HuHSC-NCG-M Model
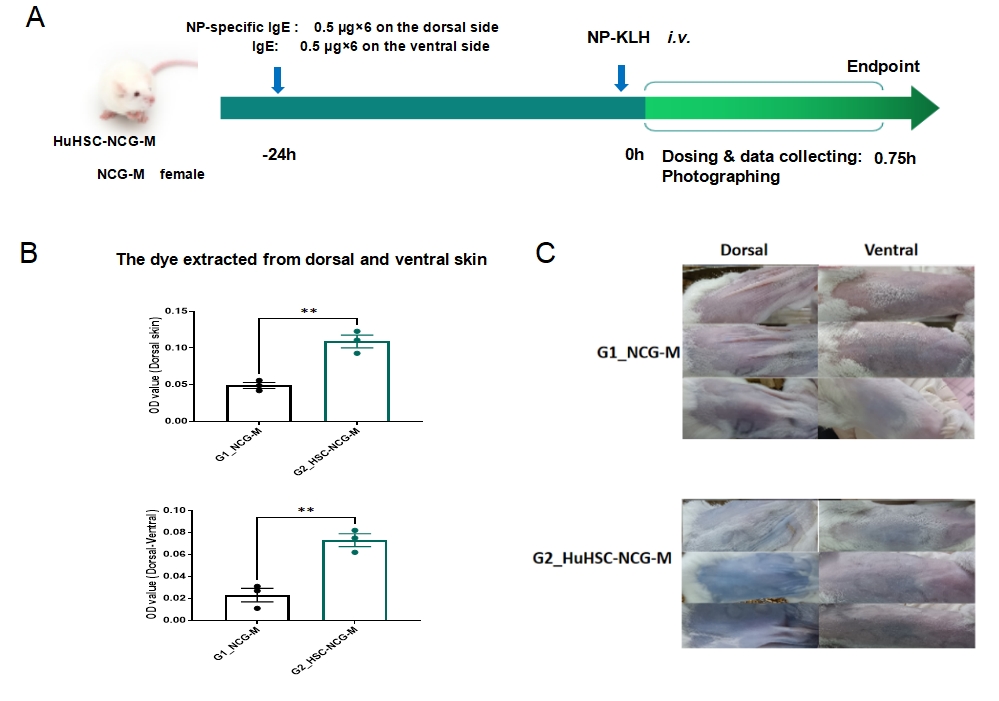
Fig.2 Anti-NP IgE-induced PCA in HSC-NCG-M mouse model
PCA model strategy is shown in Fig. 2A. Human hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) were infused into NCG-M (strain No.T036669) immunodeficient mice , to reconstitute the human immune system. The human immune system reconstituted mice were challenged with NP-specific IgE and a follow challenge with NP-KLH to establish PCA model. 0.75 h post NP-KLH administration, mice in modeling group exhibited dye leakage in dorsal skin (Fig.2B-C). Data presented as mean ± SEM. **P<0.01.