Model establishment
Experimental mouse strains: BALB/c, male
Modeling reagent: OVA
Dosing route: intratracheal instillation
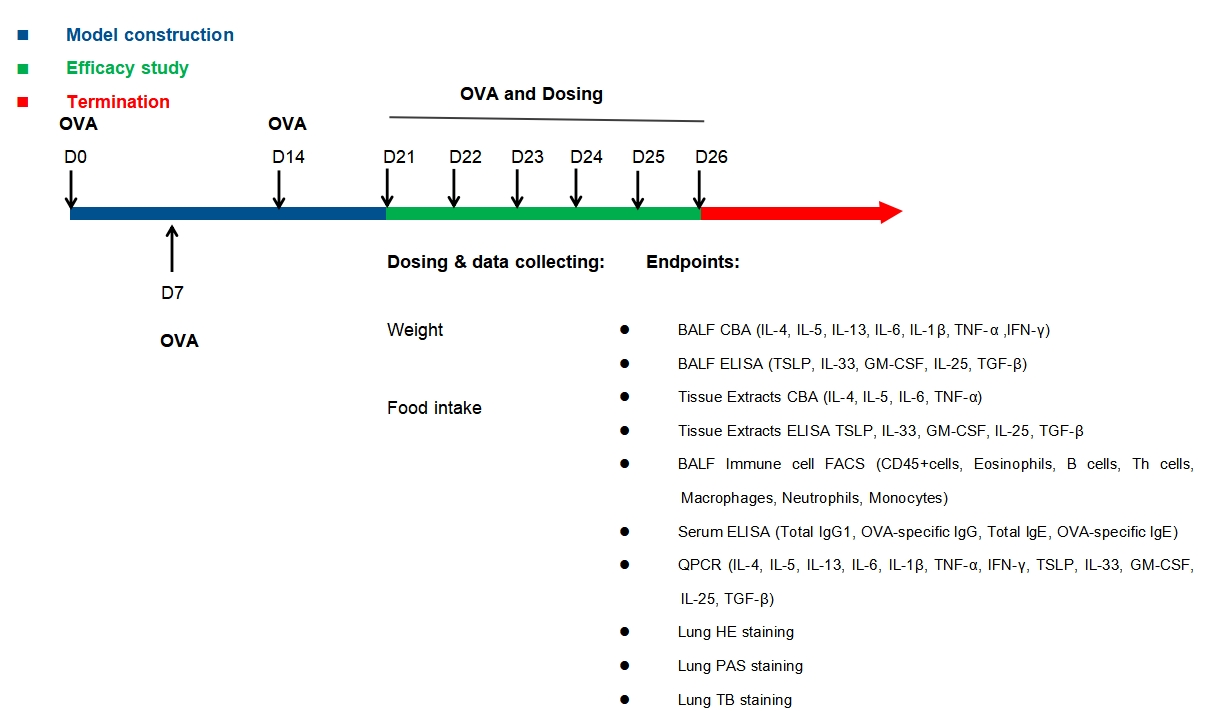
Efficacy study: Dexamethasone (DXMS)
Serum IgG1, total IgE, OVA-sIgG and OVA-sIgE
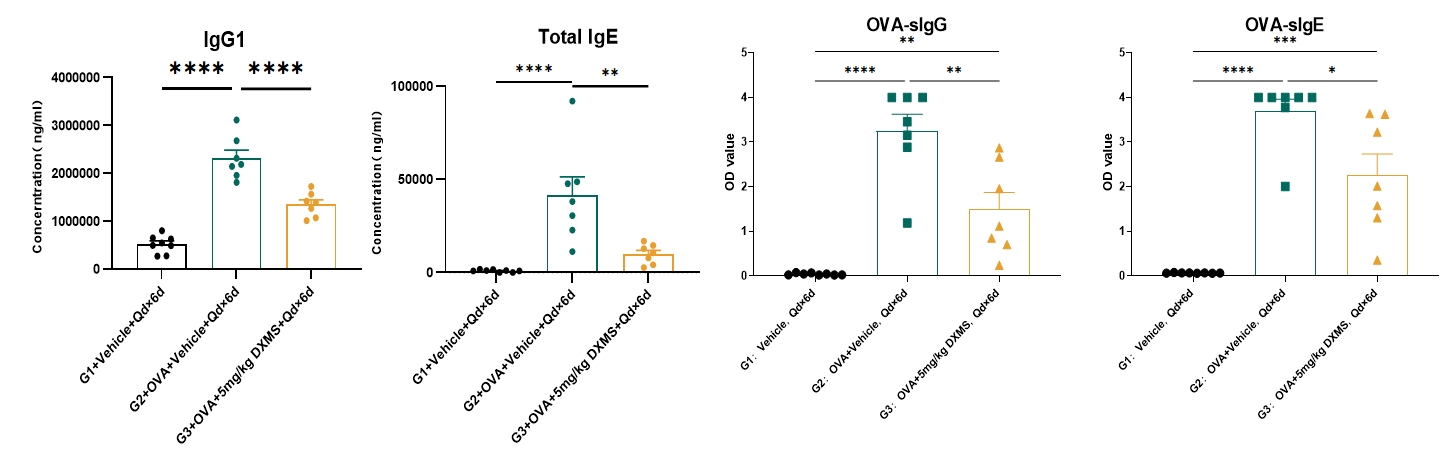
Serum levels of IgG1, total IgE, OVA-sIgG and OVA-sIgE were elevated in the OVA-induced asthma mouse model group but decreased in G3 following treatment with dexamethasone (DXMS). G1: vehicle control; G2: OVA + vehicle; G3: OVA + DXMS. Data is expressed as Mean ± SEM. Statistical analysis was performed using one-way ANOVA. P<0.05; **: P<0.01; ***: P<0.001; ****: P<0.0001.
Cytokines analysis
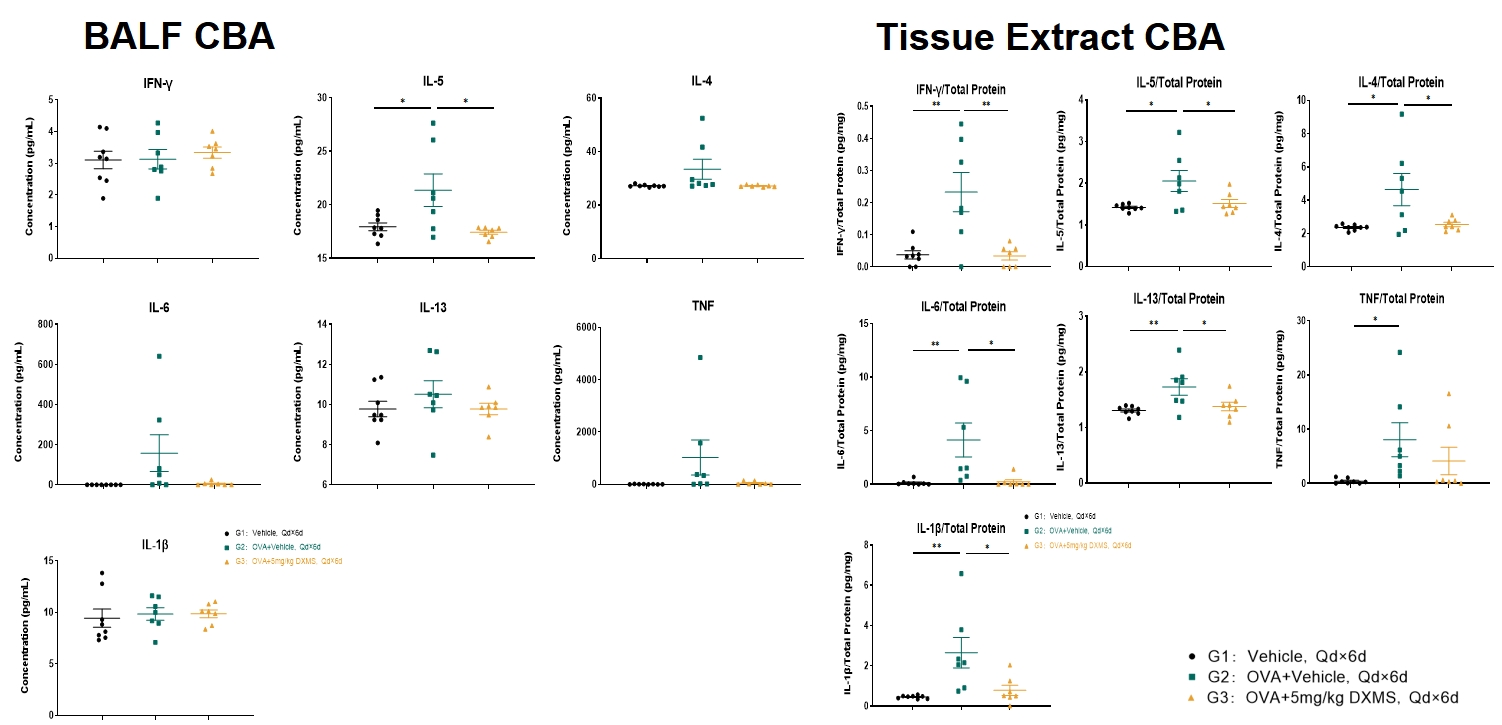
Levels of IL-5 in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) increased after OVA-induction and decreased in the DXMS treated group G3. Tissue levels of IL-33, IL-4, IL-5, IL-6, IL-13, IL-1β, IFN-γ and TNF-α increased significantly after OVA induction. Treatment with DXMS decreased tissue levels of IL-33, IL-4, IL-5, IL-6, IL-13, IL-1β and IFN-γ but not TNF-α. G1: vehicle control; G2: OVA + vehicle; G3: OVA + DXMS. Data is expressed as Mean ± SEM. Statistical analysis was performed using one-way ANOVA. P<0.05; **: P<0.01.
Histopathology
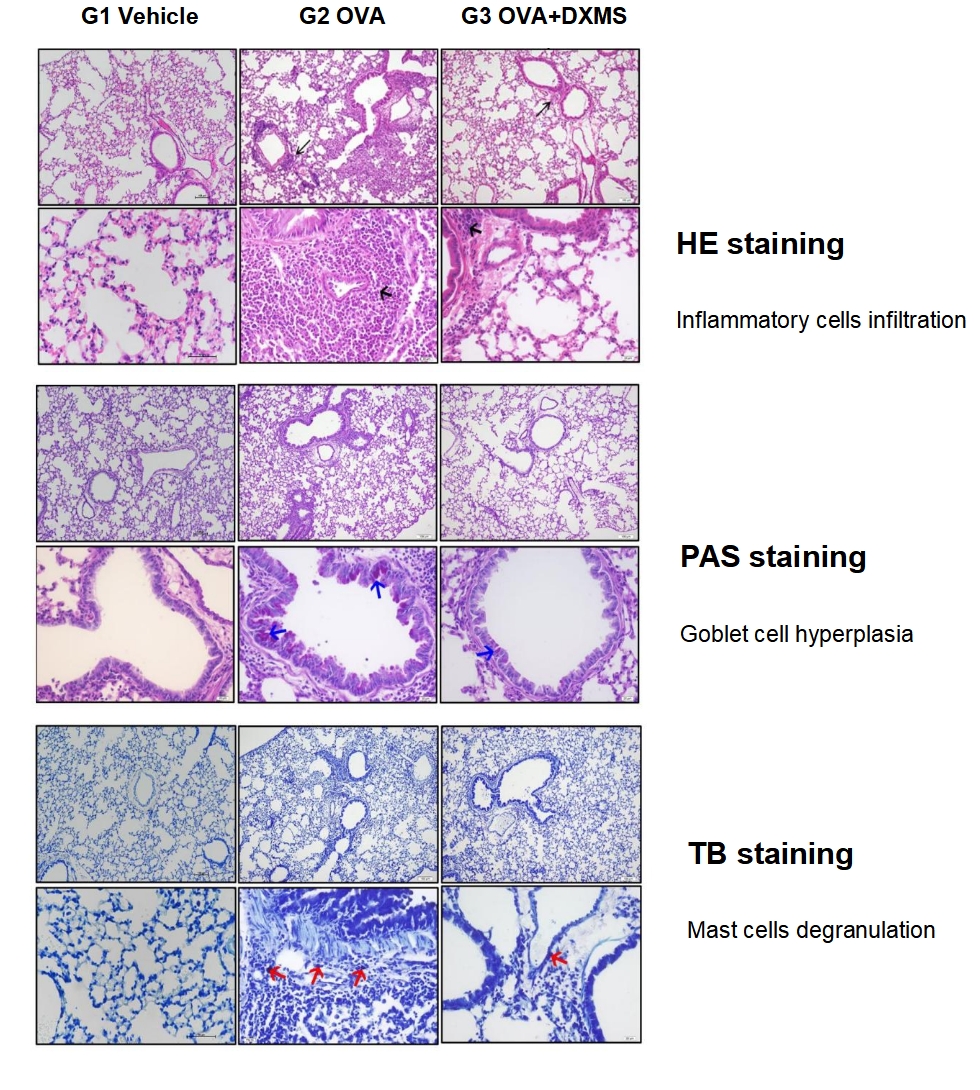
HE Staining. Inflammatory cells were showed by black arrows. Bar=100 μm in the top row. Bar=20 μm in the bottom row. Toluidine Blue Staining. Compared to G1, G2 showed moderate to massive infiltration of inflammatory cells including eosinophils, mast cells, lymphocytes, macrophages, and neutrophils surrounding the airways and vessels of the lungs. Compared to G2, G3 showed significantly reduced inflammatory cell infiltration surrounding the airways and blood vessels.
Mast cell degranulation are indicated by red arrows. Bar=100 μm in the top row. Bar=20 μm in the bottom row. Compared to G1, G2 showed occasional degranulation of mast cells in the interstitium of the lungs. Compared to G2, G3 showed rare mast cell degranulation in the interstitium of the lungs.
PAS Staining. Mucus attachment was shown by blue arrows. Bar=100 μm in the top row. Bar=20 μm in the bottom row. Compared to G1, G2 showed moderate to abundant PAS-positive mucous material in the bronchi or bronchiolar mucosal epithelium. Compared to G2, G3 showed only occasional PAS-positive mucous material in the mucosal epithelium of the bronchi or bronchioles.
Efficacy study: Anti-human CD69 antibody
Experimental mouse strains: BALB/c-hCD69 mice, both male and female
Modeling reagent: OVA
Dosing route: intratracheal instillation
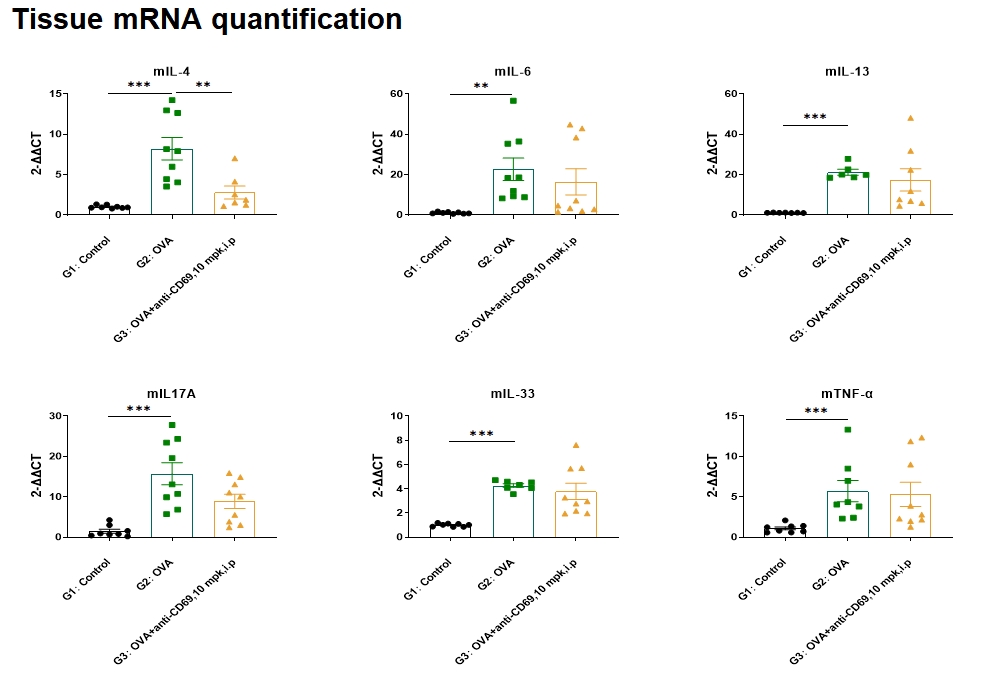
OVA-induced asthma resulted in an increase of lung IL-4, IL-6, IL-33, IL17A, and TNF-α mRNA levels. Administration of anti-CD69 antibody resulted in a decrease in lung IL-4 mRNA levels. No statistically significant decrease in IL-6, IL-33, IL17A, mRNA levels was observed with anti-CD69 antibody administration.
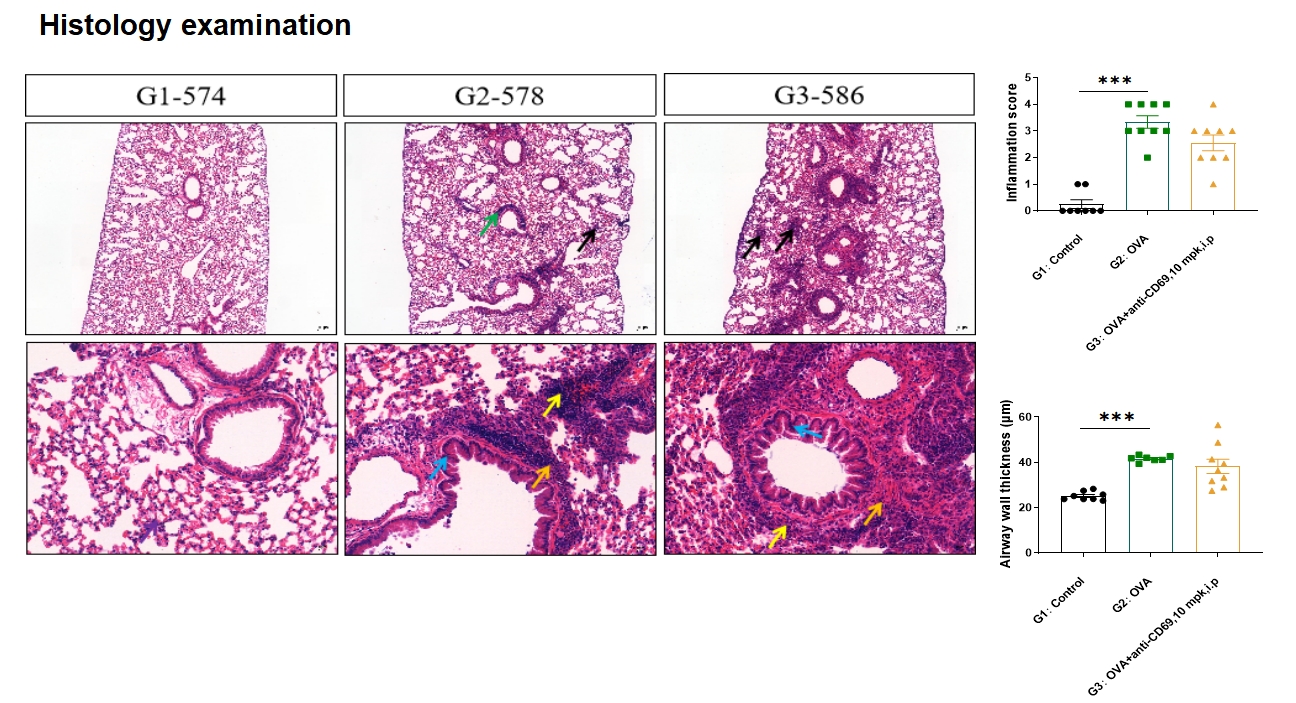
Lung HE score and airway wall thickness increased after OVA induction. No statistically significant decrease in airway wall thickness was observed with anti-CD69 antibody administration. Notes: Mucosal epithelial thickening (blue arrow), eosinophils (orange arrow), inflammatory cell infiltration (green arrow), necrotic lesion (black arrow), lymphocytes (yellow arrow); The first row: Bar=200μm; Second row: Bar=50μm.
Data is expressed as Mean ± SEM. Statistical analysis was performed using one-way ANOVA. **: P<0.01; ***: P<0.001.