Apolipoprotein E (APOE) is primarily responsible for the transport of lipoproteins, fat-soluble vitamins, and cholesterol, particularly in the central nervous system. In peripheral tissues, APOE is mainly produced on liver and macrophages and mediates cholesterol metabolism. In the brain, APOE is mainly produced by astrocytes, which transport cholesterol to neurons through APOE receptors.
Apoe KO mice are extremely sensitive to cholesterol, exhibiting deficits in scavenging chylomicron, while VLDL and LDL of plasma and cholesterol content are significantly increased. At about 3 months, fat streaks appear near the aorta forming a pre-atherosclerotic lesion with age. Older APOE-deficient mice (over 17 months) have xanthoma lesions composed of crystalline cholesterol clots, lipid droplets, and foam cells, with smaller xanthoma seen in the choroid plexus and ventral tendon. Apoe knock-out mice also demonstrate deficits in learning and memory.
Experimental Design and Example Data
1. Determination of APOE protein expression
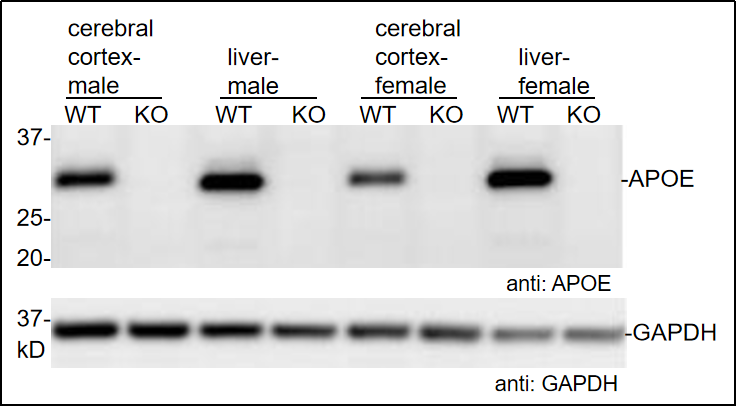
Fig 1. Protein expression of APOE in cerebrum and liver tissues.
APOE protein expression in cerebrum and liver tissues determined by Western Blot using APOE-specific antibody (Abcam, ab183596). WT: C57BL/6JGpt wildtype mice and KO: Apoe-KO homozygous mice. (Data source: Abcam collaborative verification).
2. IHC analysis of APOE
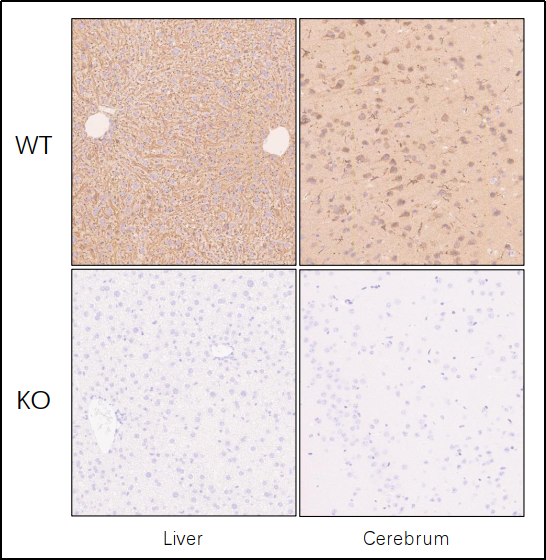
Fig 2. Representative IHC of APOE in cerebrum and liver tissues.
IHC analysis of APOE in cerebrum and liver tissues using specific antibody (Abcam, ab183596). WT: C57BL/6JGpt wildtype mice and KO: Apoe-KO homozygous mice. (Data source: Abcam collaborative verification).
3. Monitoring of body weight
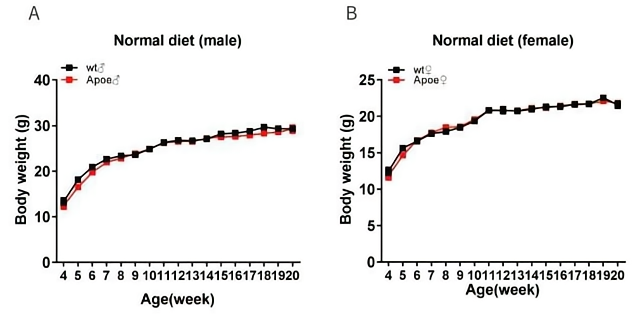
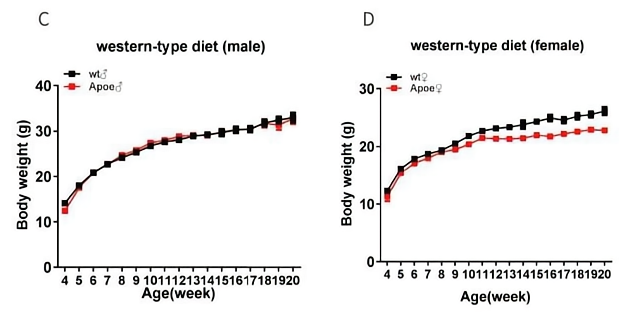
Fig3. Body weight of Apoe-KO mice across 16 weeks.
Wild-type mice and homozygous Apoe-/- mice monitored for body weight when maintained on normal diet (A&B) and western diet (D12079B:0.15% cholesterol high fat diet ) (C&D). Apoe-/- mice and wild-type mice have similar trends of body weight change.
4. Detection of blood lipid concentrations
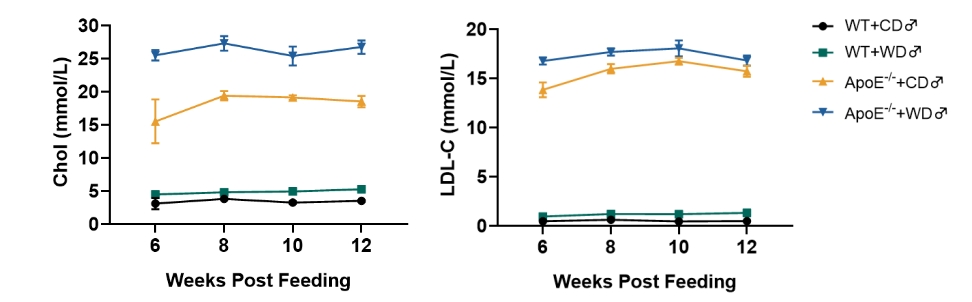
Fig 4. Detection of blood lipids in Apoe-/- mice.
Compared with wild-type mice, Cholesterol and LDL-C levels are significantly increased in Western diet (WD) (D12079B) fed Apoe-/- mice.
5. Pathology analysis
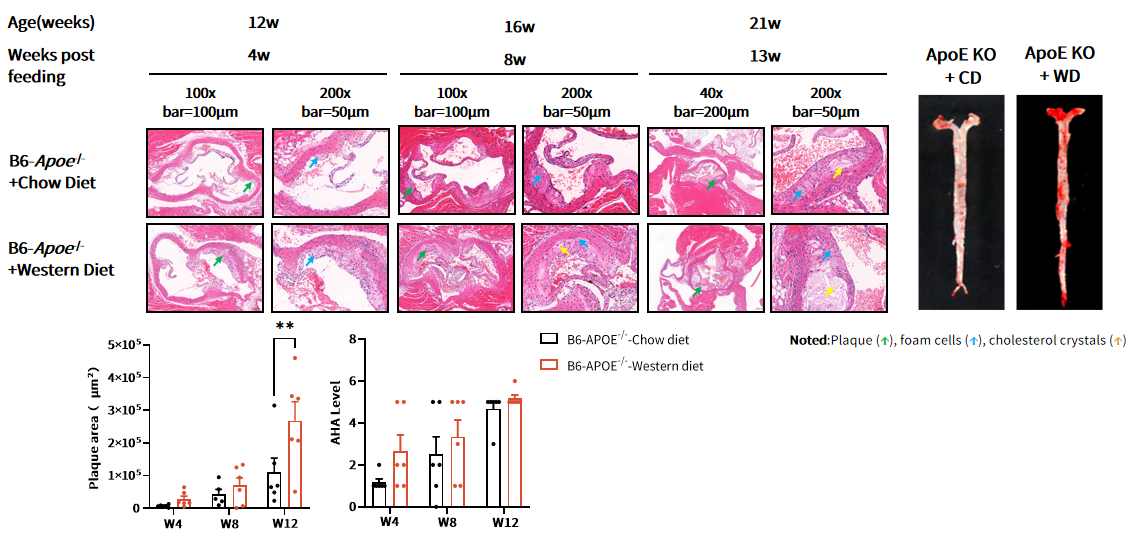
Fig 5. H&E and Oil Red O staining of Apoe-/- mice aorta.
ApoE-/- mice were fed with chow diet (CD) and western diet (WD) (D12079B) starting from 8 weeks of age. After 12 weeks of WD feeding, atherosclerotic plaques could be observed with larger area in the aortic root by H&E staining. Lipid-rich plaques (Red) also can be detected by Oil red O staining of the whole aorta. p**<0.01 by t-test.
6. Drug efficacy study
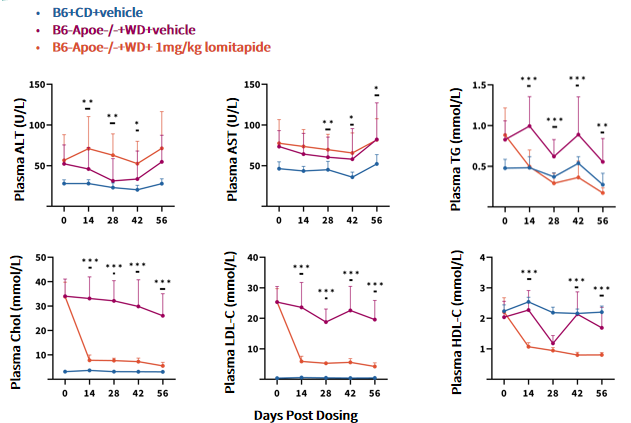
Fig 6. Lomitapide had a lipid-lowering effect on B6-Apoe-/- mice.
Data are shown as Mean±SD, analyzed by Two-Way ANOVA. B6+CD+vehicle (n=6~12♂); B6-Apoe-/-+WD+vehicle (n=9~20♂); B6-Apoe-/-+WD+1 mg/kg lomitapide (n=9~20♂) . *, **, *** represented as p<0.05, p<0.01, p<0.001 respectively.