The Low-Density Lipoprotein Receptor (known as LDL receptor or LDLR) can clear low-density lipoprotein (LDL) and intermediate-density lipoprotein (IDL) to regulate plasma cholesterol levels. Ldlr-deficient mice (Ldlr-KO) express twice the total plasma cholesterol levels of wild-type mice and are more sensitive to hypercholesterolemia. In addition, overexpression of the Ldlr gene in mice inhibits plasma hypercholesterolemia caused by a high cholesterol diet. The Ldlr-KO mouse model provides a valuable platform for the study of diabetic nephropathy, atherosclerosis, hyperlipemia and hyperglycemia.
Study Design and Example Data
Body weight
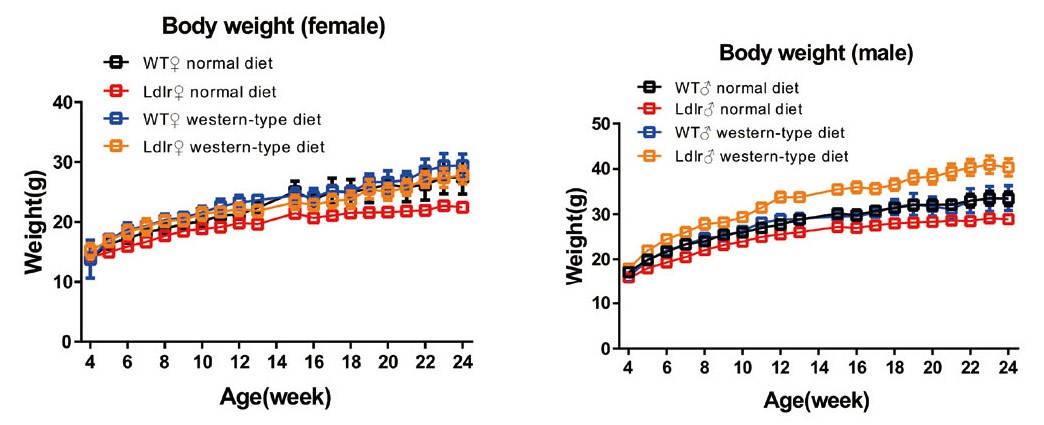
Fig 1. Body weight test of Ldlr-KO mice.
The body weight changes of wild-type mice and Ldlr ko mice under normal diet and high fat diet were measured every two weeks starting at four weeks of age. No significant difference in bodyweight was detected between Ldlr-KO and WT mice on either diet.
Oil Red O staining of Aortic arch
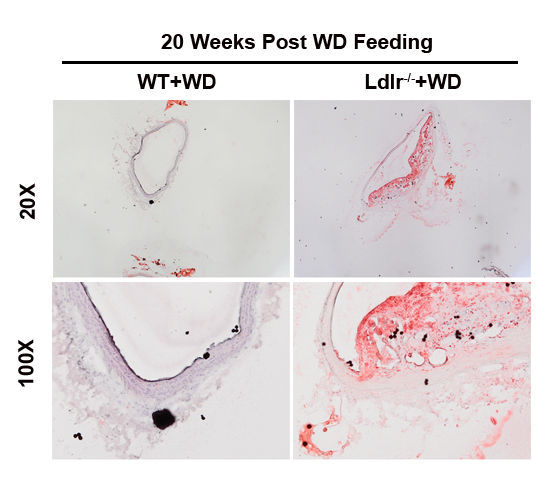
Fig 2. Observation of Aortic arch pathology with oil red O staining.
Western diet induces atherosclerosis in Ldlr knockout mice. The aortic arch of WT and Ldlr-KO mice fed high fat diet was isolated at 20 weeks, and pathological changes of the aortic wall were visualized with oil red O staining. The inner wall of the aorta of Ldlr-KO mice displays local wall thickening with lipid adhesion, reflective of the initial phenotype of atherosclerosis.
Blood lipid testing
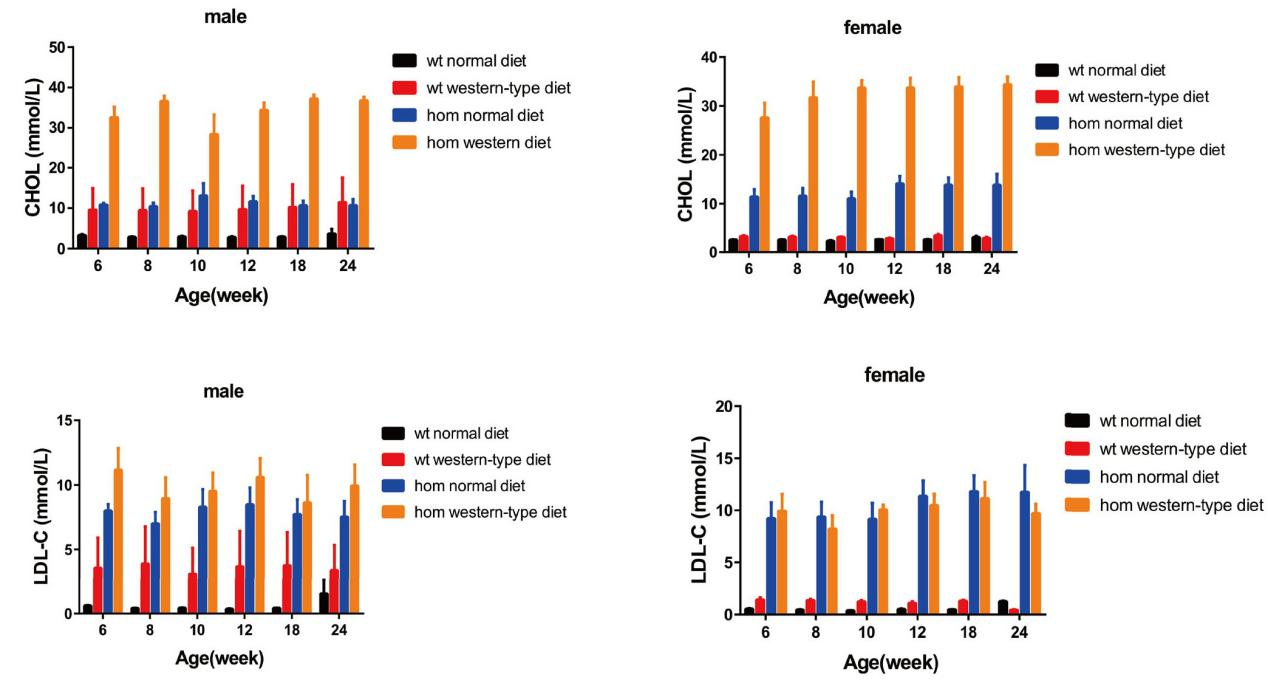
Fig 3. Blood lipid test of Ldlr mice.
Mice were divided into standard chow and Western diet groups and body weights were measured from the 4th week, and blood lipids were measured at 6, 8, 10, 12, 18, 24 weeks, respectively. Compared with wildtype male mice, cholesterol content in the blood of Ldlr-KO mice is 2-3 times higher and LDL-C content is 3-5 times higher than that of wildtype mice after 6 weeks of normal diet or high-fat diet. Compared with wild females, the levels of CHOL and LDL-C in the blood of Ldlr-/- mice is 5-10 times after 6 weeks on a normal diet or a high-fat diet. (CHOL: cholesterol; LDL-C: Low Density Lipoprotein C.)